MeSO2Cl
The formation of mesylates with methanesulfonyl chloride (MeSO2Cl) is usually accomplished with a base (ex. TEA or pyridine), in a solvent such as DCM, with cooling or at RT. A possible side-pdt is the corresponding alkyl chloride (see Alcohol to Chloride - Sulfonyl Chlorides).
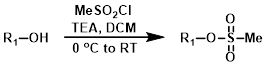
Example 1
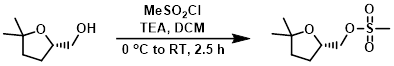
To a solution of the SM (300 mg, 2.30 mmol) in DCM (6 mL) at 0 C was added TEA (0.64 mL, 4.6 mmol) followed by MeSO2Cl (0.21 mL, 2.76 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 C for 30 min, then was allowed to warm to RT over 2 h. The mixture was quenched with H2O (10 mL) and extracted with DCM (2 x 20 mL). The combined organics were washed with H2O (20 mL), brine (20 mL), dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated. The resulting material was purified by silica gel column chromatography (35% EtOAc/hexane) to provide the product as a colorless gum. [310 mg, 64%]
[Patent Reference: WO2015129926, page 89, ![]() (21.5 MB)]
(21.5 MB)]
Example 2
MeSO2Cl (49 uL, 0.64 mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of the SM (205 mg, 0.43 mmol) and TEA (178 uL, 1.3 mmol) in dry DCM (5 mL) at 0 C under N2. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 C for 2 h, after which time H2O was added and the mixture was extracted with DCM. The org layer was dried (MgSO4) and concentrated to provide the product as a yellow solid which was taken to the next step without further purification. [280 mg]
[Patent Reference: WO2015144799, page 153, ![]() (18.8 MB)]
(18.8 MB)]
Example 3

To a solution of the SM (2.50 g, 16.4 mmol) in DCM (20 mL) was added TEA (2.75 mL, 19.7 mmol) followed by MeSO2Cl (1.53 mL, 19.7 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at RT overnight. The mixture was diluted with H2O and extracted with DCM. The combined organics were washed with brine, dried (MgSO4), and concentrated to provide the product which was taken to the next step without further purification.
[Patent Reference: WO2016014463, page 122, ![]() (6.7 MB)]
(6.7 MB)]
Example 4

To a solution of the SM (0.5 g, 2.17 mmol) in DCM (13 mL) was added TEA (0.6 mL, 4.34 mmol) and MeSO2Cl (0.2 mL, 2.6 mmol) in DCM (2 mL) at 0 C. The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 1 h. The mixture was diluted with DCM and H2O. The org layer was separated, dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to provide the product as a syrup. [0.3 g]
[Patent Reference: WO2014149164, page 398, ![]() (23.7 MB)]
(23.7 MB)]
(MeSO2)2O
Methanesulfonic anhydride conditions are typically similar to that for methanesulfonyl chloride. One benefit is that there is no possibility of forming the alkyl chloride side-pdt.
2O.png)
Example 1
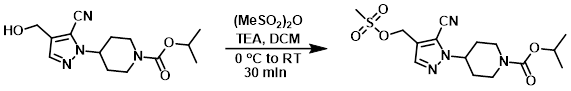
To a solution of the SM (75 mg, 0.24 mmol) in anhydrous DCM (1 mL) was added TEA (0.1 mL, 0.74 mmol). The mixture was cooled in an ice bath and treated with methanesulfonic anhydride (62 mg, 0.34 mmol). The reaction mixture was removed from the ice bath and stirred for 30 min. The mixture was quenched by the addition of sat aq NaHCO3. The layers were separated and the aq layer was further extracted with DCM (3x). The combined organics were washed with brine, dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated to provide the product as an oil which was taken forward without further purification. [75 mg]
[Patent Reference: WO2012069948, page 53, ![]() (3.9 MB)]
(3.9 MB)]
Example 2

To a solution of the SM (2.8 g, 14.0 mmol) in DCM (30 mL) at 0 C was added TEA (5.3 mL, 42.0 mmol) followed by methanesulfonic anhydride (3.7 g, 21.0 mmol). The reaction mixture was warmed to RT and stirred for 2 h. To the mixture was added sat aq NaHCO3 (100 mL). The layers were separated and the aq layer was further extracted with DCM. The combined organics were dried (MgSO4) and concentrated to provide the product. [3.8 g, 98%]




