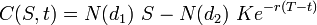Options reflect expectations about the underlying asset, and options are commonly priced using the Black-Scholes model:
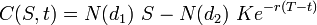
N(d1) and N(d2) are probability functions, S is the spot (current) price of the asset, K is the strike price, r is the risk free rate, and T-t represents time to maturity. Without getting into the mathematics, it suffices to say that higher volatility or expectation of volatility increases the perceived riskiness of the asset, so call options are priced lower and put options are priced higher.
Think about it intuitively. If the stock is more likely to go downwards, then there's an increased chance that the call option expires worthless, so call options must be priced lower to accommodate the relative change in expected value of the option.
Puts are priced similarly, but they move inversely with respect to call option prices due to Put-Call parity. So if call option prices are falling, then put option prices are rising (Note, however, that call prices falling does not cause put prices to rise. The inverse relationship exists because of changes in the underlying factors and how pricing works.)
So the option action signifies that the market believes the stock is headed lower (in the given time frame). That does not mean it will go lower, and option traders assume risk whenever they take a particular position. Bottom line: gotta do your own homework!
Best of luck.
在本文中,我们将解释什么是牛市看涨价差 (spread),提供详细的示例,讨论其优点
和缺点,并回答一些常见问题。
什么是牛市看涨价差 (spread)?
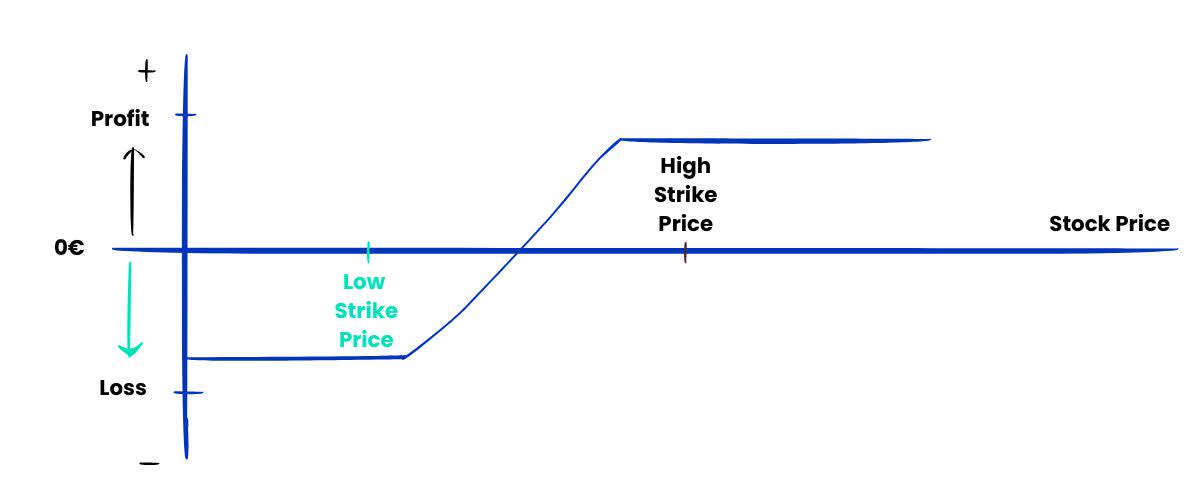
牛市看涨价差 (spread)是一种期权交易策略,旨在从标的资产价格适度上涨中利润。
该策略涉及以较低的执行价格购买 看涨期权 ,同时以较高的执行价格出售另一份到
期日相同的看涨期权。主要目标是减少支付的净溢价,从而降低交易成本。
牛市价差 (spread)限制了潜在利润和潜在损失,最大利润为执行价格减去净支付的
权利金后的差额,最大损失则限制在净支付的权利金以内。
牛市看涨价差 (spread)示例
为了更好地理解牛市看涨价差 (spread)的工作原理,让我们考虑一个例子:
假设交易者认为 XYZ 公司的股票(目前交易价为 50 美元)近期将升至 60 美元。
交易者可以按如下方式实施牛市看涨价差 (spread):
- 购买执行价格为 50 美元的看涨期权,每股支付 5 美元的溢价。
- 出售看涨期权,执行价格为 60 美元,每股溢价 2 美元。
支付的净溢价为每股 3 美元(支付 5 美元 - 收到 2 美元)。由于每个期权合约通常
代表 100 股,因此支付的净溢价总额为 300 美元。
场景:
- 股票价格上涨至 60 美元以上: 两种期权均被行使,交易者获得最大利
- 润。最大利润为 700 美元 [(执行价差 10 美元 x 100 股)- 支付的净
- 溢价 300 美元]。
- 股价保持在 50 美元至 60 美元之间: 买入的看涨期权升值,而卖出的
- 看涨期权抵消部分收益。如果股价超过 53 美元,利润将低于最大值但
- 大于零。
- 股票价格仍低于 50 美元: 两种期权均到期作废,交易者损失已支付
- 的净溢价,即 300 美元。
牛市价差 (spread)的优缺点
了解牛市看涨价差 (spread)的优点和局限性可以帮助交易者决定何时使用该策略。
| 优点 |
缺点 |
| 有限风险: 潜在损失仅限于预先知道的净支付保费。 |
有限利润: 最高利润上限为执
行价格减去支付的净溢价之间
的差额。
|
| 成本更低: 与购买单个看涨期权相比,卖出看涨期权可降低交易的总成本。 |
复杂性: 比简单地买入或卖
出单一期权更复杂。
|
| 从适度上涨中利润: 允许交易者从标的资产价格适度上涨中利润。 |
保证金要求: 由于看涨期权
的风险,这可能需要大量的保证金。
|
概括
对于预期标的资产价格温和上涨的交易者来说,牛市看涨价差 (spread)是一种有用的策略。通过了
解如何实施和管理这一策略,交易者可以限制风险,同时从市场上涨中获利。将牛市看涨
价差与其他期权策略例如熊市看涨价差进行比较,有助于交易者根据其市场前景选择最合
适的策略。
常见问题解答
1. 什么是牛市看涨价差 (spread)?
牛市看涨价差 (spread)是一种期权策略,涉及以较低的执行价格买入看涨期权并以较高
的执行价格卖出另一个看涨期权,以从标的资产价格适度上涨中利润。
2. 牛市看涨价差 (spread)如何运作?
该策略要求支付净溢价来建立交易,最大利润为执行价格减去支付的净溢价之间的差额。
最大损失仅限于支付的净溢价。
3. 牛市价差 (spread)的优点和缺点是什么?
优点包括风险有限、与购买单个看涨期权相比成本较低,以及能够从适度的价格上涨中
利润。缺点包括利润有限、复杂性和潜在的保证金要求。
4. 为何要用Skilling交易期权?
Skilling 中的 交易期权 提供高级工具、低费用和教育资源,以增强您的交易策略。了解
有关使用 Skilling 进行 CFD 交易的更多信息,以多样化您的交易机会。例如,了解 铂
金价格 可以帮助您在交易 商品 时做出战略交易决策。但是,过去的表现并不代表未来
的结果,交易也存在风险。