最新文章
文章分类
归档
2010 (264)
2011 (255)
2014 (518)
2015 (976)
2017 (946)
2019 (491)

正文
中国人 不是 蒙古人的孙子!
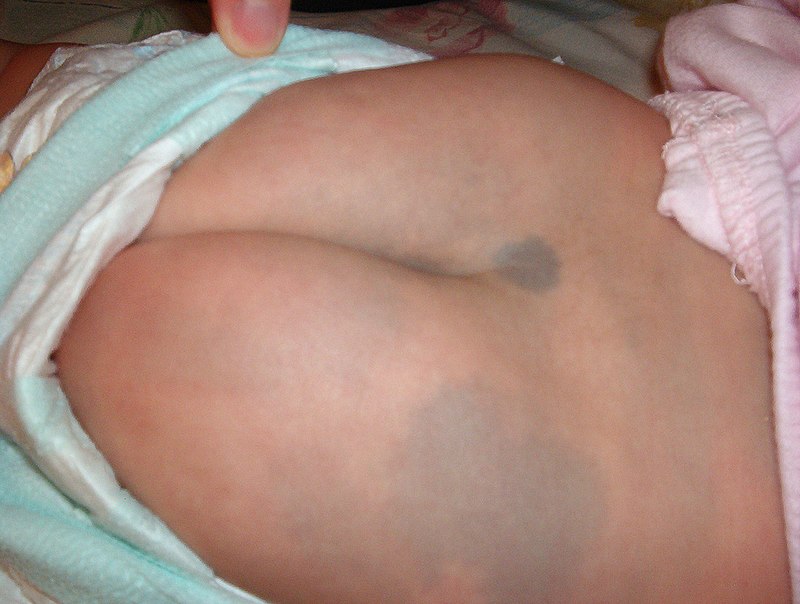
胎青 胎记 有称 蒙古斑
A Mongolian spot, also known as Mongolian blue spot,
congenital dermal melanocytosis, and dermal melanocytosis
is a benign, flat, congenital birthmark with wavy borders and irregular shape,
discovered on and named after Mongolians by Erwin Bälz.
It normally disappears three to five years after birth and almost always by puberty.
The most common color is blue, although they can be blue-gray, blue-black or even deep brown.
人种学, 是 一门较年轻的学科,只有二百来年吧,
几个分法: 根据 肤色, 地域,,,,
黑 白 黄 棕 红 五种,,,,
高加索 蒙古 黑 澳大利亚 开普 等五种,Australoid, Capoid ,Caucasoid, Mongoloid, Negroid ,,,,
有称 中国人是 蒙古人种, 白人 是高加索人种 云云,
这些 其实 几无科学性,近乎胡说,
比如, 白人 = 高加索人 = white = caucasian
Caucasian race (also Caucasoid or Europid)

高加索 位置在当今 俄罗斯的乔治亚共和国一带,近几十年才被发现是 直立人的一个地点,
一个多世纪前的 人类学家 何以将白人命名为高加索人呢?
So why do we call white people Caucasians?
The term was popularized by the German scientist
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach, (11 May 1752 – 22 January 1840)
Caucasian, the "white" race;
Mongolian, the "yellow" race;
Malayan, the "brown" race;
Ethiopian, the "black" race; and
American, the "red" race.
He considered the Caucasians to be the first race on Earth,
consistent with the common conception of the Caucasus as a place of human origin.
The Bible 圣经 describes Noah 诺亚方舟 landing his ark at a place called Mount Ararat 阿拉拉特,
which was thought by Europeans of Blumenbach's time to be on the modern Turkish-Armenian border.
(Ararat is still the name of the largest mountain in Turkey.)
In Greek mythology, Zeus 宙斯 chained Prometheus 普罗米修斯 to a rock in the Caucasus 高加索.
蒙古 是亚洲的一部分, 蒙古人是亚洲人种的一部分, 而非 亚洲人是蒙古人的一部分,
不能本末倒置。
人种的命名, 带有随意(胡说)性, 最早 想起人源人种的那几个人 说什么, 后来的就随什么而已。

德国人 克里斯托弗 .迈纳斯(Christoph Meiners (31 July 1747 – 1 May 1810))
是最先谈论人种的几个人之一。蒙古人种 (mongoloid)就是他最先提出的。
他 因某种原因 对亚洲人种的印象首先就想到了南西伯利亚蒙古高原上的黄种人。
白人=高加索人种 也是 他最先提出的。
他的人源人种说 主要有:
人种是多元的, 人种有优劣高下之分,其中 凯尔特 /塞尔特(英/爱尔兰)最高贵,其次是斯拉夫,
然后是中东/亚洲人,美洲土著是下等的,
最下等的 黑人痛觉不敏锐(耐疼),而且无表情,只不过动物般的感觉。云云。
他 是一位历史学人,哲人= philosopher,他其实不是一位真正的自然科学家,也可见他对人种学说的偏狭。
语言学, 语系说的划分 其实也是众说纷纭 不一而终,暂且不表。
=========
尽管 非洲单一人源说 当前风盛, 但多源说愈强。
比如 中国 尤其 中原华北东北西北一带 的人类起源地
基本自 河北张家口阳原县 泥河湾村
蒙古人 可能也是 根自 泥河湾
而 泥河湾村人 断不是来自 蒙古。

.jpg)
评论
目前还没有任何评论
登录后才可评论.



